Understanding the Importance of Cyber Security in Education
Cyber incidents can severely impact educational institutions, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and disruptions to teaching and learning. With schools and colleges becoming prime targets for cyber-attacks, the DfE’s updated standards aim to mitigate these risks by outlining essential practices and protocols. This guide provides an overview of the updated standards and offers practical advice for implementation.
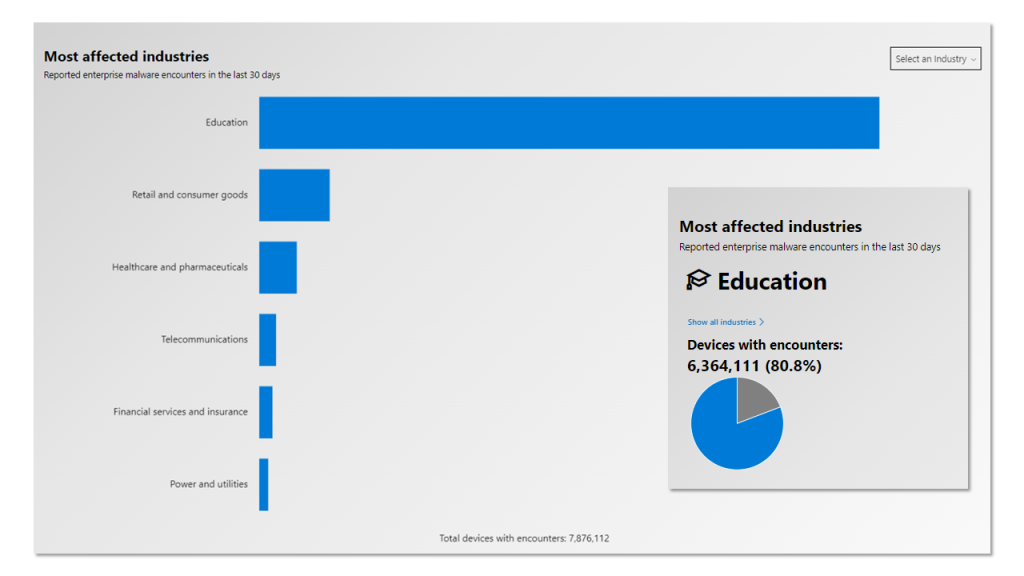
–
Understanding the Updated Standards – A Summary
Cyber security is no longer solely the domain of IT teams, and the updated standards emphasise shared responsibility across seven key areas:
–
Conducting Regular Cyber Risk Assessments:
This involves identifying potential vulnerabilities within your school’s digital infrastructure. Consider factors like user access controls, software updates, and data backups. The DfE recommends conducting a comprehensive assessment annually and reviewing it each term to stay ahead of evolving threats.
–
Developing a Cyber Awareness Plan:
Educating students and staff about cyber safety is crucial. The plan should address topics like password hygiene, phishing scams, and the importance of reporting suspicious activity. Interactive workshops, age-appropriate resources, and regular reminders can all contribute to a more cyber-aware school community.
–
Securing Technology with Anti-malware and Firewalls:
These tools act as the first line of defence against malicious software and unauthorised network access. Schools should ensure they have up-to-date anti-malware software installed on all devices and that firewalls are properly configured.
–
Controlling User Accounts and Access Privileges:
Users should only have access to the data and systems they need to perform their roles. Schools should regularly review and update user accounts and permissions to minimise potential risks.
–
Licensing and Updating Technology:
Using unlicensed software not only exposes your school to legal issues but also increases vulnerability to cyber-attacks. Ensure all software is properly licensed and updated with the latest security patches.
IMPORTANT NOTICE: As of 14th October 2025, Windows 10 will become End of Life, which means no further security/critical updates will be provided by Microsoft and certain software will remove support which could provide a significant risk of remote attacks/viruses/malware etc.
To ensure your data and networks remain secure, devices running Windows 10 should be upgraded to Windows 11 before the End-of-Life date.
Microsoft has not made the process of moving operating systems as simple as previous versions. Windows 11 features minimum hardware requirements, which are not easily replaceable before installation and support can take place. For many schools, your devices will not meet these minimum specifications and will require the replacement of most devices on your network.
To help understand the impact this may have on your school, Dataspire can assist with the identification of devices that do not meet the minimum requirements for Windows 11 and provide excellent pricing for new and refurbished devices that do. This may present an opportunity for your school to rationalise devices as well as review how and what devices are used across your school, which Dataspire is happy to assist with.
–
Data Backup and Recovery:
Regular data backups are essential for mitigating the impact of cyber-attacks or accidental data loss. Schools should establish a clear backup schedule and implement robust recovery procedures.
–
Cyber Attack Reporting:
Having a clear process for reporting potential cyber-attacks is crucial. Prompt reporting allows schools to take swift action to minimise damage and improve their defences for the future.
–
Highlighted Roles and Responsibilities
Senior Leadership Team (SLT) Digital Lead:
- Accountable for cyber security measures,
- Coordinates risk assessments and awareness training,
- Works with IT support and other stakeholders to implement standards,
IT Support:
- Executes technical requirements,
- Monitors and manages security software and devices,
- Provides technical advice and support.
- Dataspire can help
Data Protection Officer (DPO):
- Advises on data protection risks,
- Ensures compliance with data protection legislation,
- Integrating Cyber Security into the Digital Strategy,
Cyber Security should be integral to a school’s overall digital strategy. This includes aligning with other digital standards such as digital leadership and governance, cloud solutions, and server security.
–
To help you meet the standard, Dataspire recommends:
Engaging your leadership team: Secure buy-in from school leaders to ensure cyber security becomes a strategic priority. Allocate resources for training, software, and ongoing maintenance.
Assemble a cyber security team: This team, consisting of IT staff, senior leaders, and teachers, can spearhead the implementation of the standards. Seek external expertise if necessary.
Develop a comprehensive cyber security policy: The policy should clearly outline your school’s approach to cyber security, encompassing all seven DfE standards. Dataspire can help
Invest in staff training: Equip your staff with the knowledge and skills to identify and respond to cyber threats. Training should be tailored to different roles and responsibilities. Dataspire can help
Training Topics:
-
- Phishing and Social Engineering
- Password Security
- Safe use of digital devices and media
- Reporting cyber incidents
- Securing Digital Technology and Data
Create age-appropriate resources for students: Develop engaging materials that teach students about online safety and responsible digital citizenship. Consider incorporating cyber security topics into your curriculum.
Communicate the importance of cyber security: Regularly communicate the importance of cyber security to all stakeholders. Share success stories and raise awareness of potential threats.
Review and update: Cyber Security is an ongoing process. Schedule regular reviews of your cyber security measures and update your strategies based on new threats and technologies.
–
Helping You Build Your Cyber Defence
Constantly evolving threats call for constantly evolving approaches and Dataspire can help you flag and prevent security vulnerabilities and compliance gaps with confidence.
Speak to us today and find out how we can help you with:
- Dark Web Monitoring
- Vulnerability Management
- Threat Detection
- Robust Backup
- Device, Network and Application Discovery
- Patch Management
- and Comprehensive Cyber Security Support for Your School
This is a crucial issue so contact us today using the form below.
–
Conclusion
By embracing the updated DfE Cyber Security Standards and implementing the recommended actions, schools can create a safe and secure digital environment for learning.
Remember, cyber security is a shared responsibility and by adopting these we can foster a culture of security that protects students, staff, and the broader educational community.
Additional Resources:
- DfE Cyber Security Standards
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- Building your School’s Cyber Defence
- Cyber Security Cheat Sheet for School Staff
- Modern Cyber Security Terms Schools Should Know
- Online Safety Resource Guide
- DfE Filtering and Monitoring Standards
- DfE Digital Leadership and Governance Standards
- DfE Cloud Standards
- DfE Server and Storage Standards
